CHARLES BABBAGE
By Casey. S
Charles Babbage was born on December 26, 1791. Charles was having health issues so he was sent to Totnes for school in 1801. After changing schools a couple more times, he went back home to study with a personal tutor. In 1810, he began college in Cambridge. While attending college, he founded the Analytical society to promote the Leibniz notation. During this time, he also had the idea of using a machine to calculate math. Charles was able to graduate in 1814. He married Georgiana Whitmore and had 9 children and moved to London. In 1824 he helped to found Astronomical Society and he was rewarded his first gold metal. 1827 Charles created a table of logarithm from 1 to 108000. A Logarithm is a formula that is used in algebra. 1834 he founded the Statistical Society of London. 1851 he presented at The Great Exposition. In 10/18/1891 he died.
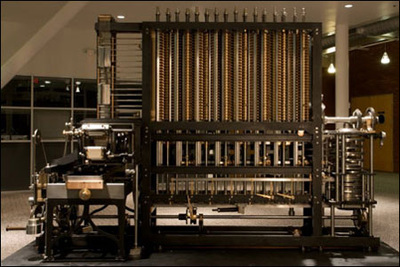
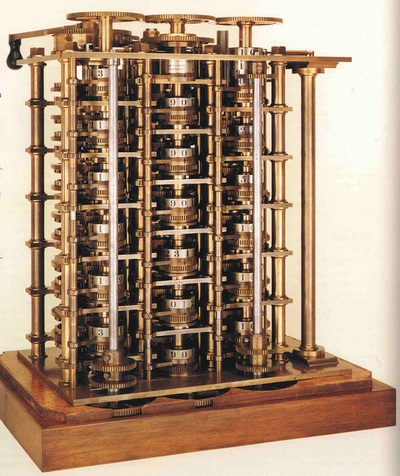
Charles Babbage is famous for inventing the Cow Catcher, the Heliograph, Analytical Engine, and the Difference Engine. Babbage was a mathematician, philosopher and inventor. Babbage first proposed his two computers which were called the Difference Engine and the Analytical Engine, both had a Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), flow control, and memory storage unit. The Difference Engine was small and movable but the Analytical Engine was big and could not be moved, both computers were done in the year of 1838.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Babbage
http://www.computerhistory.org/babbage/charlesbabbage/
http://inventors.about.com/od/bstartinventors/a/Charles_Babbage.htmhttp://www.liacs.nl/~jslob/babbage.shtml
http://www.computerhistory.org/babbage/charlesbabbage/
http://inventors.about.com/od/bstartinventors/a/Charles_Babbage.htmhttp://www.liacs.nl/~jslob/babbage.shtml
Created by Casey. s. I did Charles Babbage because I wanted to know who made the first computer.